Naphthoquinones of the spinochrome class: occurrence, isolation, biosynthesis and biomedical applications
Abstract
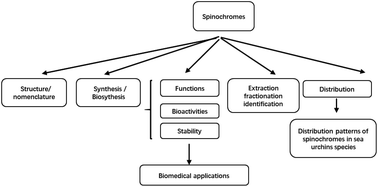
Quinones are widespread in nature and have been found in plants, fungi and bacteria, as well as in members of the animal kingdom. More than forty closely related naphthoquinones have been found in echinoderms, mainly in sea urchins but occasionally in brittle stars, sea stars and starfish. This review aims to examine controversial issues on the chemistry, biosynthesis, functions, stability and application aspects of the spinochrome class, a prominent group of secondary metabolites found in sea urchins. The emphasis of this review is on the isolation and structure of these compounds, together with evaluation of their relevant biological activities, source organisms, the location of origin and methods used for isolation and identification. In addition, the studies of their biosynthesis and ecological function, stability and chemical synthesis have been highlighted. This review aims to establish a focus for future spinochrome research and its potential for benefiting human health and well-being.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...