Selective binding of matrix metalloproteases MMP-9 and MMP-12 to inhibitor-assisted thermolysin-imprinted beads
Abstract
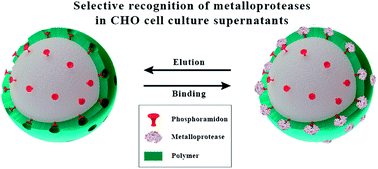
Protein-imprinted polymers have been synthesized to recognize and specifically bind selected proteins. However, protein imprinting requires substantial amounts of pure protein to efficiently obtain imprinted polymers for large scale applications, e.g. protein purification by affinity chromatography. In the absence of large quantities of a pure protein of interest, an alternative strategy was developed. In this case study, neutral metalloprotease thermolysin was selected as a commercially available surrogate for imprinting polymer beads. Phosphoramidon-assisted thermolysin-imprinted beads were synthesized. During rebinding experiments, it was shown that these beads specifically bind to thermolysin. In addition, it was shown that these beads also bind in CHO cell culture supernatant to the matrix metalloprotease-9 and -12 (MMP-9, -12). Therefore, these beads can be applied as a selective sorbent for the rare metalloproteases MMP-9 and MMP-12 to remove these proteases from CHO cell culture supernatants. The high selectivity of thermolysin-imprinted beads can be extended to other proteases of the family of metalloproteases, and is not limited to thermolysin. This innovative approach is suitable to address the challenges in the field of protease purification and isolation from biotechnologically relevant media.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...