Toxicity of fungicides to Pisum sativum: a study of oxidative damage, growth suppression, cellular death and morpho-anatomical changes
Abstract
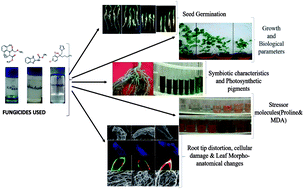
Considering the fungicidal threat to the sustainable agro-environment, the toxicological impacts of three fungicides, namely kitazin, hexaconazole and carbendazim, on the biological, chemical and morpho-anatomical changes of peas were assessed. Fungicide applications in general caused a slow but gradual reduction in growth, symbiosis and yields of peas, which, however, varied appreciably among species and concentrations of the three fungicides. Of the three fungicides, carbendazim had the most lethal effect, in which it delayed seed germination and also diminished the overall pea growth. Carbendazim at 3000 μg kg−1 maximally reduced the germination, SVI, size of roots and shoots and total dry matter accumulation in roots, shoots and whole plants distinctly by 40%, 84%, 72%, 73%, 68%, 75% and 73% (p ≤ 0.05), respectively. Hexaconazole at 120 μg kg−1 significantly (p ≤ 0.05) declined total chlorophyll, carotenoids, grain yields, grain protein, root P and shoot N by 19%, 28%, 46%, 69%, 48% and 51%, respectively, over the control. The synthesis of stress biomarkers and oxidative stress were increased with increasing dosage rates of fungicides. Proline content in roots, shoots, leaves and grains, MDA, electrolyte leakage and H2O2 of plants grown in soil treated with 288 μg kg−1 kitazin were increased significantly (p ≤ 0.05) by 73%, 52%, 41%, 24%, 59%, 40% and 27%, respectively, relative to the control. Antioxidant defence enzymes were greater in pea foliage. The SEM and CLSM images revealed an obvious alteration in root tips, enhanced cellular damage and cell death when plants were raised under fungicide stress. Also, morpho-anatomical variations in fungicide-treated foliage were visible in the SEM images. Overall, the present study suggests that a careful and secure strategy should be adopted before fungicides are chosen for enhancing pulse production in different agro-climatic regions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...