Current advances of carbene-mediated photoaffinity labeling in medicinal chemistry
Abstract
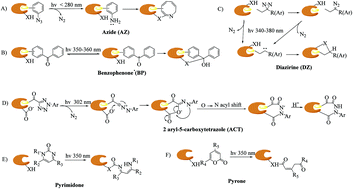
Photoaffinity labeling (PAL) in combination with a chemical probe to covalently bind its target upon UV irradiation has demonstrated considerable promise in drug discovery for identifying new drug targets and binding sites. In particular, carbene-mediated photoaffinity labeling (cmPAL) has been widely used in drug target identification owing to its excellent photolabeling efficiency, minimal steric interference and longer excitation wavelength. Specifically, diazirines, which are among the precursors of carbenes and have higher carbene yields and greater chemical stability than diazo compounds, have proved to be valuable photolabile reagents in a diverse range of biological systems. This review highlights current advances of cmPAL in medicinal chemistry, with a focus on structures and applications for identifying small molecule–protein and macromolecule–protein interactions and ligand-gated ion channels, coupled with advances in the discovery of targets and inhibitors using carbene precursor-based biological probes developed in recent decades.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...