First-principles investigations of manganese oxide (MnOx) complex-sandwiched bilayer graphene systems
Abstract
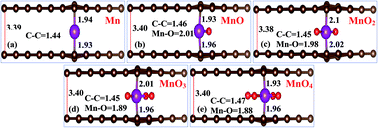
In this paper, we calculate the structural, electronic, magnetic and optical parameters of MnOx (x = 0–4), cluster-sandwiched bilayer graphene (Gr) systems, utilizing first-principles calculations with van der Waals corrections implemented with density functional theory (DFT). Charge transfer is observed from the graphene layers to the MnOx clusters, thus producing a hole doping phenomenon in the graphene layers. The MnOx clusters’ electronegative nature greatly modifies the electronic structure of bilayer graphene. It is observed that the MnOx clusters’ incorporation in bilayer graphene converts zero band gap semimetal bilayer graphene to a half metallic or dilute magnetic semiconducting material. Interestingly, the Gr/MnO3/Gr complex structure displays indirect band gap semiconductor behavior for both spin channels, and has a ∼20 meV band gap value. The band gap during spin up and spin down band channels increases as the size of MnOx is increased in between the graphene layers. Through spin density diagrams, it is revealed that the MnOx clusters’ incorporation in the graphene layers converts nonmagnetic bilayer graphene to a magnetic substrate. The obtained magnetic moments for Gr/Mn/Gr, Gr/MnO/Gr, Gr/MnO2/Gr, Gr/MnO3/Gr and Gr/MnO4/Gr, sandwiched bilayer graphene systems were found to be 3.53 μB, 3.03 μB, 2.46 μB, 1.03 μB and 0.00 μB, respectively. Through density of states (DOS) plots, it is inferred that the d orbitals of the Mn atoms are mainly responsible for the generation of magnetic moments in the given bilayer graphene systems. The optical parameters, specifically absorption, reflectivity and refractive coefficients, were obtained for all given systems. The absorption spectrum of bilayer graphene is improved in the visible range when MnOx clusters are sandwiched between the graphene layers. It is revealed that MnOx clusters’ incorporation in bilayer graphene improves these optical parameters in the low lying energy region. The results obtained during this study provide the basis for future experimental extrapolations to make multilayer graphene systems functional for optoelectronic and spintronic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...