New therapeutic strategies based on interference with telomeric DNA synthesis of tumor cells to suppress the growth of tumors
Abstract
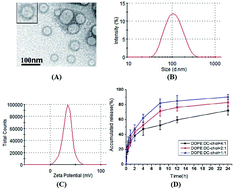
An unusual enzyme called telomerase acts on parts of chromosomes known as telomeres. The enzyme has recently been found in many human tumors and is viewed as a new target for tumor therapy. In this research, we chose the analogue of guanine “2′,3′-dideoxyguanosine” (ddG) as the telomerase inhibitor and prepared the ddG-loaded cationic nanoliposomes (ddG-Clip) to specifically target the tumor tissue and preferentially occupy the telomerase nucleotide binding site. The mean diameter of ddG-Clip is 101.54 ± 2.60 nm and they are cationically charged with a zeta potential of 34.0 ± 9.43 mV; also, the encapsulation efficiency of ddG-Clip is 53.44% ± 2.29%. In vitro cytotoxicity results show that cationic nanoliposomes by themselves are almost non-toxic, but with the increase in ddG concentration, ddG-Clip has the ability to kill S180 tumor cells. The anti-tumor activity study suggests that ddG-Clip could not only suppress the tumor growth, but also inhibit tumor liver metastasis well. In conclusion, reverse transcriptase inhibitor-loaded cationic nanoliposomes could interfere with the synthesis of telomeric DNA and block abnormal proliferation of tumor cells, therefore achieving tumor apoptosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...