Preparation of thermo-responsive drug-loaded nanofibrous films created by electrospinning
Abstract
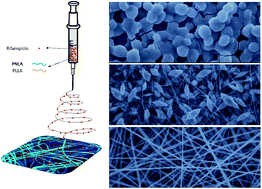
We prepared thermosensitive and biocompatible drug-loaded nanofibrous films by an electrospinning technique using a block copolymer, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly(L-lactide) (PNLA), and poly(L-lactide) (PLLA). The copolymer PNLA was synthesized by the radical polymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm), followed by the ring-opening polymerization of L-lactide. The properties of PNIPAAm and PNLA were selectively discussed based on the results of NMR, FT-IR, GPC, and CA analyses. Because of the low molecular weight of PNIPAAm and PNLA and the hydrolysis of PNLA resulting from its hydrophilicity, these copolymers were inappropriate for electrospinning separately. Hence, a mixture of PNLA and PLLA was used to prepare electrospun nanofibrous films. SEM images of the PNLA/PLLA electrospun films showed that homogeneous fibres with smooth surfaces were obtained. In vitro release studies indicated that the drug-release rate of the PNLA/PLLA electrospun nanofibrous films can be adjusted by the content and molecular weight of PNLA and by the environmental temperature. The results demonstrate that electrospinning is a promising way to create stimuli-responsive fibrous films with potential applications in the design of controllable drug delivery systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...