Influence of l-lysine on the permeation and antifouling performance of polyamide thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes
Abstract
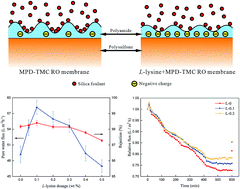
Polyamide thin film composite (TFC) reverse osmosis (RO) membranes were prepared in this study. L-Lysine is used as a type of aqueous additive during interfacial polymerization. As a result, the pure water flux (PWF) of the resulting membranes increased by around 18% and their salt rejection improved from 98.17% to 98.40% at an optimum L-lysine dosage of 0.1 wt%. Additionally, the anti-fouling properties of the resulting membranes were enhanced. The chemical structure of the membranes was investigated using attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The morphologies of the top surface and cross-section of the membranes were revealed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). Furthermore, contact angle (CA) and zeta potential measurements were carried out to determine the surface properties of the membranes. The results showed that the TFC RO membrane became thinner, smoother, smaller in surface area, more hydrophilic and more negatively charged after the introduction of L-lysine. Accordingly, the reason for the enhancement in the PWF and anti-fouling properties of the TFC RO membranes with the introduction of L-lysine was analyzed. The thinner selective layer (increase in concentration gradient across the membrane) with carboxyl groups (hydrogen bond interactions) and loose structure (greater free volume and sub-nanometer pores) resulted in low hydraulic resistance to the permeability of the polyamide selective layer, which led to the enhancement in PWF. Also, the smoother and more hydrophilic top surface and the increase in negative charges in the selective layer contribute to the improvement in anti-fouling property.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...