Se@SiO2 nanocomposites suppress microglia-mediated reactive oxygen species during spinal cord injury in rats
Abstract
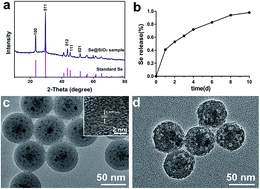
Selenium (Se) is an essential trace element with strong antioxidant activity, showing a great prospect in the treatment of spinal cord injury (SCI). However, the narrow gap between the beneficial and toxic effects has limited its further clinical application. In this experiment, we used porous Se@SiO2 nanocomposites (Se@SiO2) modified by nanotechnology as a new means of release control to investigate the anti-oxidative effect in SCI. In vitro Se@SiO2 toxicity, anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects on microglia were assayed. In vivo we investigated the protective effect of Se@SiO2 to SCI rats. Neurological function was evaluated by Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB). The histopathological analysis, microglia activation, oxidative stress, inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) and apoptosis were detected at 3 and 14 days after SCI. The favorable biocompatibility of Se@SiO2 suppressed microglia activation, which is known to be associated with oxidative stress and inflammation in vivo and in vitro. In addition, Se@SiO2 improved the rat neurological function and reduced apoptosis via caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 pathways in SCI. Se@SiO2 was able to treat SCI and reduce oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis induced by microglia activation, which may provide a novel and safe strategy for clinical application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...