Formation of bicyclic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from the reaction of a phenyl radical with cis-3-penten-1-yne†
Abstract
The formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on the C11H11 potential energy surface involved in the reactions of a phenyl radical (C6H5) with cis-3-penten-1-yne (cis-C1H![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C2–C3H
C2–C3H![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C4H–C5H3, referred to as C5H6) and its three radicals (CH
C4H–C5H3, referred to as C5H6) and its three radicals (CH![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–Ċ
C–Ċ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–CH3, CH
CH–CH3, CH![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–CH
C–CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Ċ–CH3, and cis-CH
Ċ–CH3, and cis-CH![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) C–CH
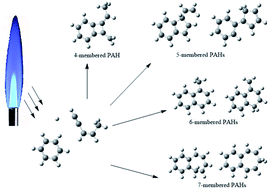
C–CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH–ĊH2, referred to as the C3-, C4-, and C5-radicals with the same chemical components, C5H5) assisted by H atoms is investigated by performing combined density functional theory (DFT) and ab initio calculations. Five potential pathways for the formation of PAHs have been explored in detail: Pathways I–II correspond to the reaction of C6H5 with C5H6 at the C1 and C2 position, and Pathways III–V involve the reaction of C6H5 with the C3-, C4-, and C5-radicals with the assistance of H atoms. The initial association of C6H5 with C5H6 or C5H5 is found to be highly exothermic with only minor barriers (1.4–7.1 kcal mol−1), which provides a large driving force for the formation of PAHs. The hydrogen atom is beneficial for the ring enlargement and ring formation processes. The present calculations predict 9 potential PAHs, six (CS6, CS10, CS13, CS26, CS28 and CS29) of which are indicated to be energetically more favorable along Pathways I, III, IV and V at low temperature. The calculated barriers for the formation of these PAHs are around 19.2–38.0 kcal mol−1. All PAHs products could be formed at flame temperature, for the medium barriers are easily overcome in various flame conditions. The theoretical results supplement the PAH formation pathway and provide help to understand PAH growth mechanism.
CH–ĊH2, referred to as the C3-, C4-, and C5-radicals with the same chemical components, C5H5) assisted by H atoms is investigated by performing combined density functional theory (DFT) and ab initio calculations. Five potential pathways for the formation of PAHs have been explored in detail: Pathways I–II correspond to the reaction of C6H5 with C5H6 at the C1 and C2 position, and Pathways III–V involve the reaction of C6H5 with the C3-, C4-, and C5-radicals with the assistance of H atoms. The initial association of C6H5 with C5H6 or C5H5 is found to be highly exothermic with only minor barriers (1.4–7.1 kcal mol−1), which provides a large driving force for the formation of PAHs. The hydrogen atom is beneficial for the ring enlargement and ring formation processes. The present calculations predict 9 potential PAHs, six (CS6, CS10, CS13, CS26, CS28 and CS29) of which are indicated to be energetically more favorable along Pathways I, III, IV and V at low temperature. The calculated barriers for the formation of these PAHs are around 19.2–38.0 kcal mol−1. All PAHs products could be formed at flame temperature, for the medium barriers are easily overcome in various flame conditions. The theoretical results supplement the PAH formation pathway and provide help to understand PAH growth mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...