Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of AV6 derivatives as novel dual reactivators of latent HIV-1†
Abstract
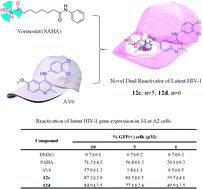
The “shock and kill” strategy might be a promising therapeutic approach for HIV/AIDS due to the existence of latent viral reservoirs. A major challenge of the “shock and kill” strategy arises from the general lack of clinically effective latency-reversing agents (LRAs). The 2-methylquinoline derivative, antiviral 6 (AV6) has been reported to induce latent HIV-1 expression and act synergistically with a HDAC inhibitor VA to reverse HIV latency. We report herein the design and identification of AV6 analogues which possess the zinc-binding group of HDAC inhibitors and have dual acting mechanism for the reactivation of HIV-1 from latency. Evaluation of compounds for the reactivation of HIV-1 latency identified two excellent active compounds 12c and 12d. Further bioassays revealed that these two compounds reactivated latent HIV-1 through dual mechanism, the inhibition of HDACs and NFAT-required for early HIV-1 gene expression. Additionally, it was found that 12c and 12d could reactivate HIV-1 transcription by releasing P-TEFb from the inactive complex 7SK snRNP. At last, molecular docking identified their orientation and binding interactions at the active site of HDAC2. This experimental data suggests that 12c and 12d can be served as effective HIV-1 LRAs which can be taken up for further studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...