Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation studies of novel F-18 labeled tumor imaging agents targeting focal adhesion kinase (FAK)†
Abstract
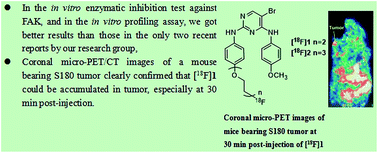
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) has been identified as a promising target in the early diagnosis and therapy of tumor. In this work, we obtained and evaluated another two novel pyrimidine-based F-18 labeled tumor imaging agents targeting FAK. Among them, the corresponding F-19 standards [19F]2, displayed inhibition of FAK with IC50 values of 57.1 nM (better than the results in our published work) and showed an good selectivity profile against some other kinds of cancer-related kinases. [18F]2 also had relatively good results in the in vivo biodistribution in S180-tumor-bearing mice, with tumor uptake of 5.40 ± 0.12 and 5.96 ± 0.09 % ID per g at 15 and 30 min post-injection, respectively. What's more, [18F]2 could be accumulated in tumor at 30 min post-injection, which could be observed from the coronal micro-PET images of mice bearing S180 tumor. In addition, the blocking study for the [18F]2 with PF-562271 (one of the well-known best selective FAK inhibitor), displayed distinct reduction in the uptake of the radiotracer in tumor at 30 min post-injection in mice, suggesting that the uptake of [18F]2 in tumor was due to FAK over-expression or high expression in tumor. And the results of the molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and the docking studies were in consistent with the changing trends of the interaction between the F-19 standards and the FAK. Finally, in order to further increase the uptake of the F-18 labeled tracer in tumor, the following points should arouse attention, which could also be considered as the new findings and contributions of this study to the field of the tumor imaging agents: (1) the F-18 labeled tumor radiotracers which have closer interaction with the FAK, should be further designed, via building of models such as 3D-QSAR model to make reasonable guidance to our drug design and consideration of some functional groups which have hydrogen-bonding or salt-bridge interactions with key residues in the kinase domain of FAK; (2) the F-18 radiotracers with better pharmacokinetic properties should be designed, via building of dynamic drug absorption and distribution model in different tissues, to predict whether the molecules have ideal absorption in tumor and low uptake in non-target tissues. The relevant study is being undertaken.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...