Immune response effects of diverse vaccine antigen attachment ways based on the self-made nanoemulsion adjuvant in systemic MRSA infection†
Abstract
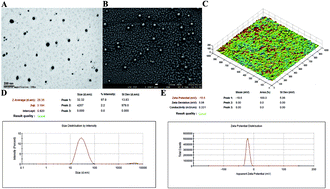
Nanoemulsion adjuvants-based vaccines have potent induced immune responses against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection. However, the efficacies and immune responses of different antigen-attaching ways on self-made nanoemulsion adjuvants remain unknown. In this study, we designed three formulations of nanoemulsion adjuvants (encapsulation, mixture, and combination) to explore their immune response-enhancing effects and their underlying mechanism in a systemic infection model of MRSA. Our results showed that the three nanoemulsion-attachment ways formulated with a fusion antigen of MRSA (HlaH35LIsdB348–465) all improved humoral and cellular immune responses. When compared with the mixture and combination formulations, the nanoemulsion-encapsulation group effectively promoted the antigen uptake of dendritic cells (DCs) in vitro, the activation of DC in draining lymph nodes and the delayed release of antigen at injection sites in vivo. Moreover, the encapsulation group induced a more ideal protective efficacy in a MRSA sepsis model by inducing more potent antibody responses and a Th1/Th17 biased CD4+ T cell response when compared with the other two attachment ways. Our findings suggested that the encapsulated formulation of vaccine with nanoemulsion adjuvant is an effective attachment way to provide protective immunity against MRSA infection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...