Enhanced dispersive solid phase extraction assisted by cloud point strategy prior to fluorometric determination of anti-hepatitis C drug velpatasvir in pharmaceutical tablets and body fluids†
Abstract
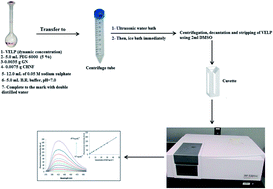
An innovative spectrofluorometric method was developed for the analysis of a recently FDA approved anti-hepatitis C velpatasvir (VELP). The developed method was relied on dispersive solid phase extraction (dSPE) using synergistic effect of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) and cobalt hydroxide nanoparticles (CHNPs) in addition to cloud point extraction (CPE) using polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG 6000) as non-ionic surfactant. This method combines the merits of preconcentration and interferences elimination achieved by dSPE and CPE, respectively. All relevant parameters such as surfactant concentration, ionic strength, pH, incubation time and others were thoroughly investigated and optimized. Fluorometric detection of VELP was carried out at excitation wavelength of 350 nm and emission wavelength of 415 nm. Under the optimum conditions, a linear calibration curve was achieved in the range of 0.5–45 ng mL−1. Limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ) based on three and ten times the standard deviation of the blank were 0.040 and 0.112 ng mL−1, respectively. This method was successfully applied for determination of VELP in real samples such as tablets, human plasma and urine samples with good recoveries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...