High sensitivity glucose detection at extremely low concentrations using a MoS2-based field-effect transistor
Abstract
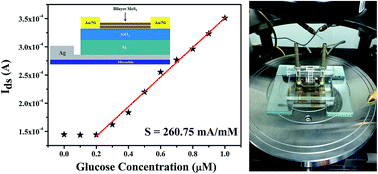
In recent years, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) based field-effect transistors (FETs) have attracted much attention because of the unique properties of MoS2 nano-materials as an ideal channel material. Using a MoS2 FET as a glucose solution biosensor has the advantages of high sensitivity and rapid response. This paper is concerned with the fabrication of a bilayer MoS2-based FET and the study of its application in the high sensitivity detection of an extremely low concentration glucose solution. It was found that the source-drain current (Ids) increases as the concentration of the glucose solution increases at the same gate voltage (Vgs) and drain voltage (Vds). The sensitivity of the biosensor as high as 260.75 mA mM−1 has been calculated and the detection limit of 300 nM was measured. The unknown concentration of a glucose solution was also detected using data based on the relationship between Ids and glucose solution concentration. In addition, many significant advantages of the biosensor were observed, such as short response time (<1 s), good stability, wide linear detection range (300 nM to 30 mM) and the micro-detection of glucose solutions. These unique properties make the bilayer MoS2-based FET a great potential candidate for next generation biosensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...