Implications of designing a bromelain loaded enteric nanoformulation on its stability and anti-inflammatory potential upon oral administration
Abstract
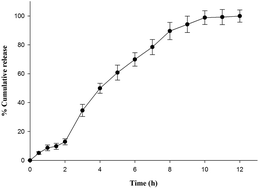
The objective of the present investigation was to develop an enteric nano-formulation of bromelain to improve its stability and anti-inflammatory potential. Bromelain loaded nanoparticles (Br-NPs) were developed using a Eudragit L 100 polymer by a double emulsion solvent evaporation method to obtain gastro-resistant properties. Br-NPs were characterized for particle size (248.89 ± 22.76 nm), zeta potential (−27.34 ± 2.17 mV), entrapment efficiency (85.42 ± 5.34%), surface morphology (spherical) and in vitro release profile. Infrared spectroscopy confirmed the entrapment of bromelain while thermal and pXRD analysis concomitantly corroborated the reduced crystallinity of bromelain in nanoparticles. Formulations showed gastro-resistant behavior at gastric pH and sustained bromelain release up to 10 h in phosphate buffer at pH 6.8 and followed Higuchi square root release kinetics. The optimized lyophilized formulation ensured 2 year shelf-life at room temperature. In vivo studies revealed significantly improved performance of entrapped bromelain in inhibiting carrageenan induced paw edema by mitigating leucocyte migration and release of nitric oxide, TNFα and IL-1β in paw compared to bromelain solution. In conclusion, enteric Br-NPs could be a viable drug delivery system for effective oral bromelain delivery in inflammatory conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...