Investigation on enhanced photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A with bismuth oxyiodide catalyst using response surface methodology†
Abstract
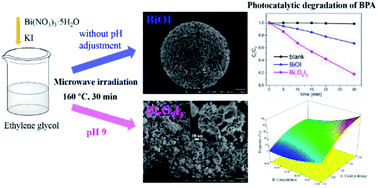
In this study, Bi7O9I3 photocatalyst was successfully synthesized via a simple and rapid microwave irradiation method. The characterization of prepared photocatalysts was determined by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS), UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) and photoluminescence (PL). The photocatalytic performance was determines by the degradation of bisphenol A (BPA) under xenon lamp illumination. The Bi7O9I3 catalyst exhibited superior photocatalytic performance and the first-order kinetic rate constant of Bi7O9I3 was about 4.2 times greater than that of BiOI. The enhanced photocatalytic activity was associated with surface morphology, suitable band gap energy and low recombination rate of electron–hole pairs. Furthermore, the photocatalytic efficiency of BPA with Bi7O9I3 was systematically investigated using a three factor, three level Box–Behnken experimental design and response surface methodology (RSM). A quadratic polynomial model was proposed. Experimental and predicted values exhibited a good correlation with a predicted R2 value of 0.9016. A relative significance study of three independent variables showed that catalyst dosage had the most significant positive effect on the degradation of BPA, followed by initial concentration of BPA and pH value. The prepared Bi7O9I3 is a promising photocatalyst for practical application in organic pollutant decomposition.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...