In situ preparation of Ag nanoparticles on silicon wafer as highly sensitive SERS substrate
Abstract
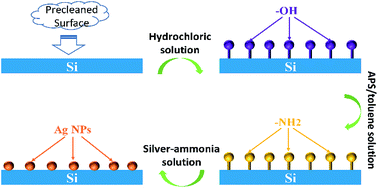
An intensive surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect is realized by ordered Ag nanoparticles (NPs) in situ grown on silicon wafer directly using (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APS) as both the surface modifier and reducing agent. The as-prepared ordered Ag NPs based SERS substrate shows excellent performance in detecting glycerin (an important integration in liquid super lubricating system) as well as conventional Rhodamine 6G (R6G, a kind of dye organic pollutant). The enhancement factor (EF) achieves 4-fold for glycerin and 10-fold for R6G (allowing for detecting as low as 10−11 M aqueous R6G), confirming the high sensitivity. The limited relative standard deviations (RSD) of the enhancement factors are within 15% for both glycerin and R6G, indicating the excellent uniformity. This remarkable progress is ascribed to the advantages of APS in improving adsorption and modulating distribution of Ag NPs on silicon, which results in a large local electric field to enhance the Raman signals. The SEM and UV-visible absorption spectrum characterization verified the contribution of APS in SERS improvement by investigating the influence of APS content and reduction time during the preparation process. All these advances imply that the SERS substrates prepared by Ag NPs in situ grown on silicon wafer have great potential application in real-time interface state tracing and sensitive detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...