Metabonomic strategy for the detection of metabolic effects of probiotics combined with prebiotic supplementation in weaned rats†
Abstract
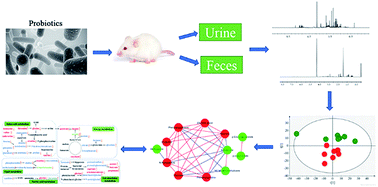
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effects of probiotics combined with prebiotics (PP) supplementation on weaned rat metabolism. A metabonomic strategy employing 1H-NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis was used to examine weaned rat biological responses to PP supplementation. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (post-natal day 21, PD 21) received probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM (L-NCFM) and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 (B-LBi07), 1 : 1, 1.0 × 1011 cfu kg−1) and prebiotics (Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP), Poria cocos polysaccharides (PCPs) and Lentinan, 1 : 1 : 1, 24 g kg−1) via intragastric administration for 28 consecutive days. Urine and feces were collected for analysis. Significant topographical metabolic variations were present in urine and feces. Urinary metabolites upregulated by PP treatment included alanine, N-acetylglycine, glutamine, dimethylamine, phosphorylcholine, ethylene glycol, mannitol, phenylacetylglycine and glycoate, which were related to alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, and choline metabolism. Feces-derived metabolites, including caproate, valerate, butyrate, propionate, lactate, acetate, succinate, methanol, threonine and methionine, were significantly increased, which were related to short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) metabolism and TCA cycle metabolism. These results indicate that dietary PP supplementation can regulate common systemic metabolic processes, including energy metabolism, amino acid metabolism, lipid metabolism, nucleic acid metabolism, and gut microbiota-related metabolism. This study also illuminates the vital role of PP supplementation in regulating the metabolism of weaned rats.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...