Highly sensitive p-type 4H-SiC van der Pauw sensor
Abstract
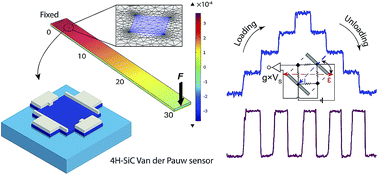
This paper presents for the first time a p-type 4H silicon carbide (4H-SiC) van der Pauw strain sensor by utilizing the strain induced effect in four-terminal devices. The sensor was fabricated from a 4H-SiC (0001) wafer, using a 1 μm thick p-type epilayer with a concentration of 1018 cm−3. Taking advantage of the four-terminal configuration, the sensor can eliminate the need for resistance-to-voltage conversion which is typically required for two-terminal devices. The van der Pauw sensor also exhibits an excellent repeatability and linearity with a significantly large output voltage in induced strain ranging from 0 to 334 ppm. Various sensors aligned in different orientations were measured and a high sensitivity of 26.3 ppm−1 was obtained. Combining these performances with the excellent mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and chemical inertness of 4H-SiC, the proposed sensor is promising for strain monitoring in harsh environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...