Boosting efficiency and stability using zirconia nanosphere-held carbon for proton exchange membrane fuel cells
Abstract
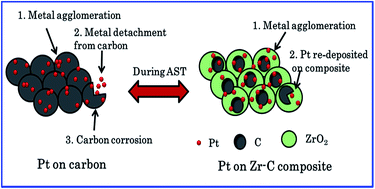
The synthesis of a zirconia-held carbon supported Pt electrocatalyst increases the fuel cell performance in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. The pure tetragonal phase of the zirconia–carbon composite is synthesized using a low temperature method. The optimum composition of zirconia–carbon exhibits a maximum peak power density of 1.12 W cm−2 with a metal (Pt) loading of 150 μg cm−2. This also improves long time durability and retains 70% of its initial activity even after 6000 potential cycles between 1 to 1.6 V vs. a dynamic hydrogen electrode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...