CVD growth of continuous and spatially uniform single layer graphene across the grain boundary of preferred (111) oriented copper processed by sequential melting–resolidification–recrystallization
Abstract
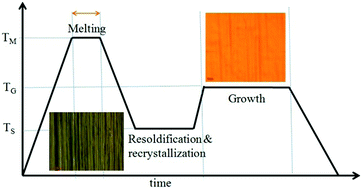
The properties of the catalyst used for CVD growth have a significant influence on the quality of the graphene grown. Single crystallinity or preferred (111) orientation with a smooth surface is the most essential criterion for the growth of high quality graphene on a copper substrate. Herein, the effective strategy of pre-heat treatment of the copper substrate for the growth of improved quality single layer graphene is demonstrated. The sequential melting, resolidification and recrystallization with a controlled slow cooling rate leads to preferred (111) oriented grain growth in the copper substrate, which was confirmed with XRD studies. The grain growth evolution and strain relaxation, correlated with surface smoothening, were inferred from AFM studies. The Raman spectroscopy measurement signifies the improved quality of the CVD grown graphene which is almost free from the multilayer patches that are usually associated with the routine CVD growth process. The Raman mapping carried out directly on the graphene/copper surface reveals spatial continuity and uniformity of graphene quality across the copper grain boundaries over a large area, which signifies the importance of the strain relaxed improved surface morphology with a uniform catalytic and crystallographic environment of the underlying surface. The electrical characterization corroborates the result of improved quality of graphene grown on recrystallized copper. Hence, a feasible process of high quality graphene growth was achieved with a simple but effective strategy of preheat treatment involving melting, resolidification and recrystallization of the copper substrate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...