A new antimony-based organic–inorganic hybrid absorber with photoconductive response†
Abstract
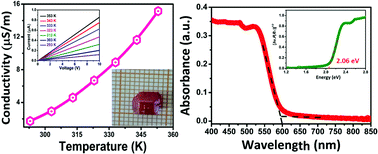
Organic–inorganic hybrid perovskites (most notably CH3NH3PbI3) have recently been demonstrated as high-performance and low cost hybrid materials for photovoltaic application because of their prominent light-absorbing capacity and excellent optoelectronic properties. However, some serious concerns, including the potential toxicity of lead and chemical/phase instability of such hybrid perovskites, have become bottlenecks for their commercialization. In this study, through utilizing an alternative trivalent cation Sb3+ with the ns2np0 electronic configuration, we designed a new lead-free hybrid material, [tert-butylammonium]4[Sb4I16]·2H2O (1), which adopts a zero-dimensional architecture consisting of corner-sharing SbI6 octahedra. It is noteworthy that 1 shows evident light-absorbance with a narrow optical bandgap of ∼2.06 eV, along with positive temperature-dependent conductivity and notable photo-conductive response. Moreover, 1 displays phase stability under ambient conditions, which is superior to that of CH3NH3PbI3. The obtained results suggest the potential of 1 as a light absorbing material for photovoltaic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...