Luminescent metal–organic frameworks as chemical sensors: common pitfalls and proposed best practices
Abstract
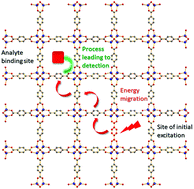
The ever-increasing need to determine and monitor the chemical constituents of the constantly evolving environment has led the global scientific community to invest considerable research effort in the development of efficient and user-friendly chemical sensors. The development of improved chemical sensors largely depends on the synthesis of novel materials with the ability to transform a molecular recognition event into a readable signal. Among the various types of sensory materials, those where analyte detection is based on the change of a luminescence signal are gaining increasing attention due to the extremely high sensitivities which can be achieved in combination with new technological advances enabling the integration of optical detection systems in small, portable and easy to use devices. In this critical review we approach the emerging field of sensory materials based on luminescent metal–organic frameworks (LMOFs) by beginning with a survey of the general principles of luminescence-based sensing. In particular, after a brief overview, we first focus on the working principles and successes of well established sensory materials based on small molecules and conjugated polymers. Subsequently, we concentrate on the special features of LMOFs which make them promising sensory materials and we discuss best practices which researchers in the field should follow in order to prove the sensing ability of LMOFs and avoid common misconceptions and errors. We continue with presenting selected examples of LMOF-based sensors for nitroaromatics, humidity and heavy metal ions from the recent literature and we conclude with a summary of the state-of-the-art of LMOF sensors. Finally, we propose some directions for future research on LMOF sensors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers Review-type Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...