Synthesis of well-defined PCL-b-PnBA-b-PMMA ABC-type triblock copolymers: toward the construction of nanostructures in epoxy thermosets†
Abstract
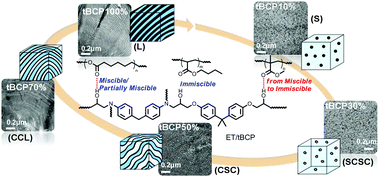
In this study we prepared a novel triblock copolymer (tBCP) through ring-opening polymerization (ROP) with ε-caprolactone (ε-CL) and two specific atom transfer radical polymerizations (ATRPs), with n-butyl acrylate (nBA) and methyl methacrylate (MMA), respectively (herein, a supplemental activator and reducing agent and halogen-exchange ATRPs were employed). These chain-extending polymerizations were chosen to achieve controlled/living polymerization. This strategy afforded a well-defined ABC-type PCL-b-PnBA-b-PMMA tBCP (Mn, GPC = 56 600; PDI = 1.18) comprising two external miscible blocks with an epoxy monomer and a middle soft block. After curing with the diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-A and 4,4′-methylenedianiline, the miscibility of the resulting epoxy thermoset (ET)/tBCP composites was examined using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermogravimetric analysis. On further examining the ET/tBCP microstructures using transmission electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering, we observed transitions with a long range order—from lamellar to core/shell cylinder to short core/shell cylinder morphologies—upon increasing the amount of ET. The domain sizes obtained after the curing reaction were in the range of approximately 30–60 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...