Ultraviolet light-, temperature- and pH-responsive fluorescent sensors based on cellulose nanocrystals
Abstract
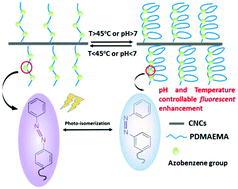
A novel CNC-g-P(AzoC6MA-co-DMAEMA) fluorescent nanosensor was synthesized by the atom transfer radical copolymerization (ATRP) reaction of AzoC6MA and DMAEMA with cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) modified with 2-bromoisobutyryl groups (CNC-Br) as the initiators. The characterization of environmentally sensitive CNC-g-P(AzoC6MA-co-DMAEMA) fluorescent nanosensor was studied, and its responses to ultraviolet (UV) light, temperature and pH were investigated. Under irradiation of UV light, the CNC-g-P(AzoC6MA-co-DMAEMA) fluorescent nanosensor exhibited isomerization of molecular structures of azobenzene groups and reversible transformation of fluorescence intensity. Due to the temperature- and pH-responsive properties of P(AzoC6MA-co-DMAEMA) side chains in the graft copolymers, the microenvironment of azobenzene groups in the fluorescent nanosensors could be changed through adjusting the external temperature or pH, which led to a reversible change in the fluorescence intensity of the nanosensors. This type of simple, cheap, dispersible and sensitive fluorescent nanosensor has potential advantages of in situ detection and monitoring of temperature or pH in organisms or water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...