Enzyme-driven biodegradable nanomotor based on tubular-shaped polymeric vesicles†
Abstract
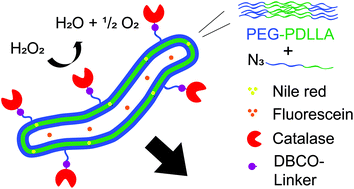
Various nanomotors that can mimic the motion of natural systems have recently been proposed. Yet, most designs are metal based and not applicable in biological settings. We report the first biodegradable nanomotor that moves in the presence of fuel. Tubular-shaped polymersomes with 5 wt% azide handles were assembled with catalase chemically linked to the handles. The nanotubes move autonomously in H2O2.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Frontiers in Supramolecular and Macromolecular Science symposia


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...