Carotenoid biosynthesis of pak choi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis) sprouts grown under different light-emitting diodes during the diurnal course†
Abstract
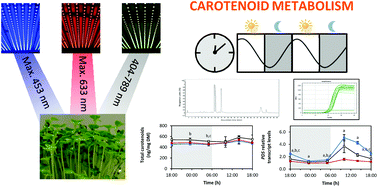
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are considered the future of greenhouse lighting. This study investigates the carotenoid concentrations of pak choi sprouts after growth under blue, red and white LEDs at six different time points. Furthermore, the diurnal changes of RNA transcripts of key genes of the carotenoid biosynthesis pathway as well as of the carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase 4 (CCD4) gene and of the transcription factor genes elongated hypocotyl 5 (HY5) and circadian clock associated 1 (CCA1) were investigated. The carotenoid concentrations were steady throughout the day, but showed a small maximum in the afternoon. An average total carotenoid concentration of 536 ± 29 ng mg−1 DM produced under white LEDs was measured, which is comparable to previously described field-grown levels. The carotenoid concentrations were slightly lower under blue or red LEDs. Moreover, the diurnal RNA transcript rhythms of most of the carotenoid biosynthesis genes showed an increase during the light period, which can be correlated to the carotenoid maxima in the afternoon. Blue LEDs caused the highest transcriptional induction of biosynthetic genes as well as of CCD4, thereby indicating an increased flux through the pathway. In addition, the highest levels of HY5 transcripts and CCA1 transcripts were determined under blue LEDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...