Selective sensing of nitric oxide by a 9,10-phenanthroquinone–pyridoxal based fluorophore†
Abstract
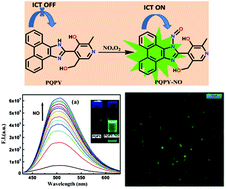
In this article, we have designed and synthesized a new, convenient and efficient phenanthroquinone–pyridoxal based fluorogenic probe PQPY, highly suitable for the selective and sensitive detection of nitric oxide in an aerated aqueous (7 : 3/H2O : MeCN) medium at pH 7.0 (10 mM HEPES buffer). Upon addition of nitric oxide, this probe exhibits emission in the green region (λem = 505 nm) which is ascribed to ICT (intramolecular charge transfer) from the phenanthroquinone moiety to the imidazole –N–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O fragment. The apparent formation constant, Kf, of the NO product of the ligand is (1.00 ± 0.2) × 105 M−1 and the LOD is 78 nM. The substantial enhancement of the life-time of the ligand (τ0 = 2.68 ns) occurs due to binding with nitric oxide (τ0 = 3.96 ns). This probe is low cytotoxicity, cell permeable and suitable for living cell imaging application.
O fragment. The apparent formation constant, Kf, of the NO product of the ligand is (1.00 ± 0.2) × 105 M−1 and the LOD is 78 nM. The substantial enhancement of the life-time of the ligand (τ0 = 2.68 ns) occurs due to binding with nitric oxide (τ0 = 3.96 ns). This probe is low cytotoxicity, cell permeable and suitable for living cell imaging application.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...