Synthesis of near-infrared fluorescent rhodamines via an SNArH reaction and their biological applications†
Abstract
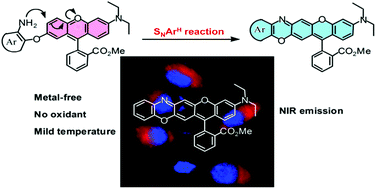
Near-infrared (NIR) dyes are of great interest in biomedicine due to diminished interfering absorption and fluorescence from biological samples, reduced scattering, and enhanced tissue penetration depth. In this context, we report the synthesis of rectilinearly π-extended rhodamine dyes using a unique intramolecular nucleophilic substitution of aromatic hydrogen (SNArH) strategy. The strategy makes use of an SNArH reaction between a preorganized aromatic amino nitrogen and an electron-deficient carbon in the xanthylium ion. The SNArH reaction presented herein can be performed under mild conditions without a transition metal catalyst and can be expected to enable the preparation of a wide variety of π-extended near-infrared fluorescent rhodamine dyes. Using this strategy, seven rectilinearly π-extended rhodamines (RE1–RE7) that had fluorescence emission wavelengths in the near-infrared region were synthesized. RE1, RE3, and RE4 were lysosome targetable and showed good photostabilities. In addition, using dye RE1 as a precursor, we constructed a novel NIR fluorescent turn-on probe (RE1-Cu), which can be used for detecting Cu2+ in living cells, demonstrating the value of our NIR functional fluorescent dyes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...