Guanidine functionalized anthranilamides as effective antibacterials with biofilm disruption activity†
Abstract
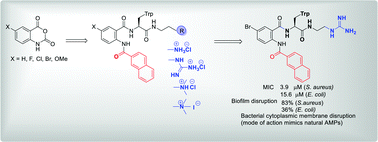
We describe a library of amphiphilic anthranilamide compounds as antimicrobial peptide (AMP) mimics. These contain a hydrophobic naphthoyl side chain and different hydrophilic cationic groups such as amino, quaternary ammonium and guanidino groups. These are prepared via the ring-opening of different isatoic anhydrides. The antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli of compounds containing guanidino cationic groups was greater than that for amino and quaternary ammonium cationic groups. The fluoro-substituted guanidinium compound 9b showed a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 2.0 μM against S. aureus, and reduced established biofilms of S. aureus by 92% at 64 μM concentration. The bromo-substituted guanidinium compound 9d exhibited good MIC against S. aureus (3.9 μM) and E. coli (15.6 μM) and disrupted established biofilms of S. aureus by 83% at 62.4 μM concentration. Cytoplasmic membrane permeability studies suggested that depolarization and disruption of the bacterial cell membrane could be a possible mechanism for antibacterial activity and the in vitro toxicity studies against MRC-5 human lung fibroblast cells showed that the potent compounds are non-toxic against mammalian cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
