Mild synthesis of silyl ethers via potassium carbonate catalyzed reactions between alcohols and hydrosilanes†
Abstract
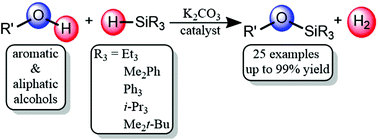
A method has been developed for the silanolysis of alcohols using an abundant and non-corrosive base K2CO3 as a catalyst. Reactions between a variety of alcohols and hydrosilanes generate silyl ethers under mild conditions. The use of hydrosilanes leads to the formation of H2 as the only byproduct thus avoiding the formation of stoichiometric strong acids. The mild conditions lead to a wide scope of possible alcohol substrates and good functional group tolerance. Selective alcohol silanolysis is also observed in the presence of reactive C–H bonds, lending this method for extensive use in protection group chemistry.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Catalysis & biocatalysis in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
