A morphological, enzymatic and metabolic approach to elucidate apoptotic-like cell death in fungi exposed to h- and α-molybdenum trioxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
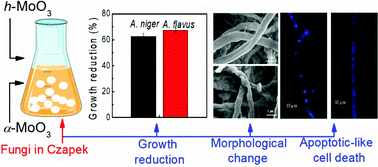
The present study compares for the first time the effects of h-MoO3 and α-MoO3 against two fungal strains: Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus flavus. The h-MoO3 nanoparticles were more toxic to both fungi than α-MoO3. The toxic effects of h-MoO3 were more pronounced toward A. flavus, which presented a growth inhibition of 67.4% at 200 mg L−1. The presence of the nanoparticles affected drastically the hyphae morphology by triggering nuclear condensation and compromising the hyphae membrane. Further analysis of the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) produced by both fungi in the presence of the nanomaterials indicated important metabolic changes related to programmed cell death. These nanomaterials induced the production of specific antifungal VOCs, such as β-Elemene and t-Cadinol, by the fungi. The production of essential enzymes involved in fungal metabolism, such as acid phosphatase, naphthol-As-BI-phosphohydrolase, β-galactosidase, β-glucosidase and N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, reduced significantly in the presence of the nanomaterials. The changes in enzymatic production and VOCs corroborate the fact that these nanoparticles, especially h-MoO3, exert changes in the fungal metabolism, triggering apoptotic-like cell death responses in these fungi.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...