Fluorescent Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for an alkaline phosphatase assay and embryonic stem cell identification based on the inner filter effect†
Abstract
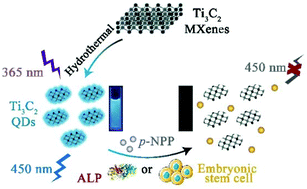
As an emerging two-dimensional material, MXenes have attracted much attention due to their unique physicochemical properties, but their application in biosensing has been lagging far behind because of their poor salt tolerance. Herein, a titanium carbide MXene quantum dot (Ti3C2 QD)-based fluorescent probe for the alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity assay and embryonic stem cell (ESC) identification was developed by taking advantage of the inner filter effect (IFE). Ti3C2 QDs with ∼4.2 nm in diameter were prepared from Ti3C2 MXenes by hydrothermal treatment, exhibiting excellent salt tolerance, anti-photobleaching and dispersion stability in aqueous solution. Owing to the remarkable overlap between the absorption spectrum of p-nitrophenol (p-NP) and the excitation and emission spectrum of Ti3C2 QDs, p-NP generated from ALP-catalyzed dephosphorylation of the substrate, p-nitrophenyl phosphate (p-NPP), can effectively quench the fluorescence of Ti3C2 QDs through the IFE. As a result, sensitive fluorometric analysis of ALP activity was achieved without complicating the conventional colorimetric ALP detection system. The proposed assay was successfully applied to determine ALP activity with a low limit of detection (0.02 U L−1) as well as monitoring the enzyme activity in real time. Finally, accurate analysis of ALP, the biomarker of ESC, in ESC lysates was also achieved using this IFE-based method, affording an alternative method for ESC identification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...