Atomic-engineered gold@silvergold alloy nanoflowers for in vivo inhibition of bacteria†
Abstract
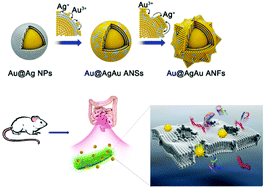
The problems of multidrug-resistant bacteria and environmental pollution associated with the abuse of antibiotics call for effective antibiotic alternatives. Here, gold@silvergold alloy nanoflowers (Au@AgAu ANFs) with distinct atomic structures are first fabricated and then demonstrated for in vivo inhibition of bacteria. The Au@AgAu ANFs display high antibacterial activity against the model Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli, with a minimum inhibitory concentration value of 4.8 μg mL−1, which is 3.1 times lower than that of silver nanoparticles. The alloy structure with a rough surface enables Au@AgAu ANFs to firmly adhere to the bacterial surface and damage the cell membrane, resulting in long-term (48 h) and highly stable (30 days) antibacterial activity. Meanwhile, the Au@AgAu ANFs show remarkable biocompatibility with human cells even at a high concentration of 40 μg mL−1. Application of Au@AgAu ANFs in the treatment of bacterial infections in the mouse intestine significantly reduces the reproduction of bacteria compared to an untreated mouse, giving results similar to those of the current antibiotic treatment, with no cytotoxicity. Our study opens up a new avenue for the rational design of safe and highly efficient antibacterial materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...