Carbon dots derived from tobacco for visually distinguishing and detecting three kinds of tetracyclines†
Abstract
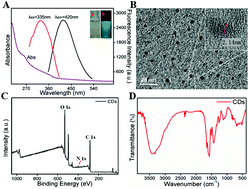
Although a number of methods to perform assays of tetracyclines using fluorescent probes have been reported, approaches for discriminating and detecting tetracyclines are few. Herein, bright-blue fluorescent carbon dots (CDs) with a quantum yield (QY) of up to ∼27.9% were hydrothermally synthesized using tobacco as the carbon source. Importantly, the as-prepared carbon dots were employed as a fluorescent probe, enabling selective differentiation of three tetracyclines using a test strip and the related quantitative detection. Towards the mechanism, three kinds of tetracyclines showed different interactions with the CDs, leading to variations in their fluorescence emissions. To be specific, the fluorescence of CDs was quenched by tetracycline (TC) without a fluorescence shift (Em = 440 nm), which was caused by an inner filter effect rather than a change in the energy band gap. Moreover, the introduction of chlorotetracycline (CTC) resulted in a blue shift (Em = 415 nm) of the fluorescence of the CD; this phenomenon was induced by the enlarged energy band gap. The CDs also responded to oxytetracycline (OTC), and their corresponding fluorescence experienced a red shift (Em = 500 nm) due to the narrowed band gap. Consequently, a visual detection strategy for three tetracyclines has been proposed based on the quantitative evaluation of TC, OTC, and CTC concentrations in broad range from 6 × 10−6 to 4 × 10−9 M, 2 × 10−6 to 2 × 10−8 M, and 2 × 10−7 to 2 × 10−8 M, respectively. Moreover, we have successfully applied the current CDs for visually distinguishing the three tetracyclines on a test strip on the basis of CDs exhibiting three types of fluorescence (weak-blue, navy-blue, and chartreuse).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...