Layered tin monoselenide as advanced photothermal conversion materials for efficient solar energy-driven water evaporation†
Abstract
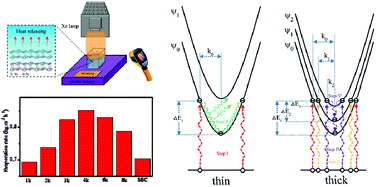
Solar energy-driven water evaporation lays a solid foundation for important photothermal applications such as sterilization, seawater desalination, and electricity generation. Due to the strong light–matter coupling, broad absorption wavelength range, and prominent quantum confinement effect, layered tin monoselenide (SnSe) holds a great potential to effectively harness solar irradiation and convert it to heat energy. In this study, SnSe is successfully deposited on a centimeter-scale nickel foam using a facile one-step pulsed-laser deposition approach. Importantly, the maximum evaporation rate of SnSe-coated nickel foam (SnSe@NF) reaches 0.85 kg m−2 h−1, which is even 21% larger than that obtained with the commercial super blue coating (0.7 kg m−2 h−1) under the same condition. A systematic analysis reveals that its good photothermal conversion capability is attributed to the synergetic effect of multi-scattering-induced light trapping and the optimal trade-off between light absorption and phonon emission. Finally, the SnSe@NF device is further used for seawater evaporation, demonstrating a comparable evaporation rate (0.8 kg m−2 h−1) to that of fresh water and good stability over many cycles of usage. In summary, the current contribution depicts a facile one-step scenario for the economical and efficient solar-enabled SnSe@NF evaporation devices. More importantly, an in-depth analysis of the photothermal conversion mechanism underneath the layered materials depicts a fundamental paradigm for the design and application of photothermal devices based on them in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...