Synthesis of a Pt/reduced graphene oxide/polydopamine composite material for localized surface plasmon resonance and methanol electrocatalysis
Abstract
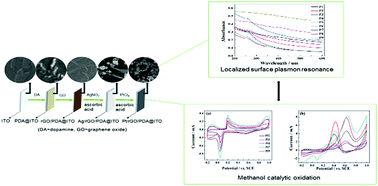
A Pt/rGO/PDA@ITO composite of Pt nanoparticles (NPs), reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and polydopamine (PDA) has been obtained on indium tin oxide glass (ITO). Firstly, a rGO/PDA@ITO composite of rGO and PDA on ITO was formed by immersing ITO into a dopamine solution at room temperature and then a graphene oxide (GO) suspension solution in a water bath at 60 °C for 3 h. Ag NPs were then deposited on the rGO/PDA@ITO surface by immersing rGO/PDA@ITO in an AgNO3 aqueous solution with the aid of ascorbic acid. Finally, Pt/rGO/PDA@ITO was obtained by immersing Ag/rGO/PDA@ITO in a platinum tetrachloride solution in the presence of ascorbic acid. Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) of the Pt NPs has been found at 260 nm from UV-visible spectra. Cyclic voltammetry curves of Pt/rGO/PDA@ITO and UV absorption peaks of the Pt NPs implied that the sample with the strongest LSPR is the optimal electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. Cyclic voltammetry of Pt/rGO/PDA@ITO showed that the ratio of current intensity between the forward scan and reverse scan peaks (If/Ib) was 1.768, indicating the remarkable anti-poison property of Pt/rGO/PDA@ITO as an electrocatalyst. Its electrochemical active surface area can reach 2.60 m2 g−1 at a scan rate of 50 mV s−1. It was found that the current decreased only 38.7% after 200 cycles. The better stability also confirmed the superior tolerance of carbon monoxide and catalytic activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...