Enhanced photocatalytic performance of bismuth vanadate assisted by polyoxometalates and phthalocyanine†
Abstract
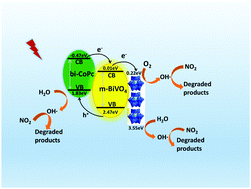
In this study, H3PW12O40 (PW12) and binuclear phthalocyanine (bi-CoPc)-modified nanofilms PW12–BiVO4–bi-CoPc were prepared by a modified metal–organic decomposition method. The photocatalytic performances of BiVO4 and PW12–BiVO4–bi-CoPc have been investigated by photocatalytic degradation of nitrogen dioxide under visible light irradiation. The PW12 could act as an electron acceptor and transfer electrons, while the bi-CoPc functioned as a hole-transporting material to enhance the photocatalytic activity of bismuth vanadate. Under illumination with visible light, PW12–BVO–bi-CoPc nanofilms exhibit a 3-fold enhancement in photocatalytic degradation of NO2. Transient photocurrent experiments and fluorescence spectroscopy were also performed to confirm the above conclusions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...