The novel and efficient reduction of graphene oxide using Ocimum sanctum L. leaf extract as an alternative renewable bio-resource
Abstract
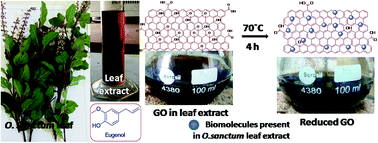
The efficient, rapid, bio-inspired synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheets was explored using green leaf extract of Ocimum sanctum L. (Tulsi leaves). This mild biorenewable reducing agent containing eugenol, ascorbic acid, and polyols also acts as a stabilizer for the prepared rGO. Characterization of the synthesized graphene nanosheets was performed using XPS, TEM, SEM, XRD, FT-IR, Raman and UV-vis spectroscopy studies. The catalytic application of the prepared rGO was established through the fruitful reduction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes to the corresponding allylic alcohols in aqueous media. Excellent yields of pure products (92%) in addition to regioselective reduction were practically observed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...