Highly hydrothermal stable mesoporous molecular sieves (TZM) prepared by the self assembly of zeolitic subunits from ZSM-5 desilication and their catalytic performance for CO2 reforming of CH4†
Abstract
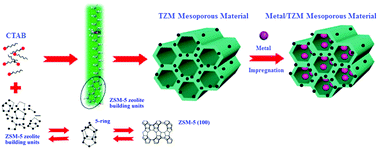
We demonstrated a new strategy for the preparation of highly stable mesoporous molecular sieves (TZM) by the desilication of ZSM-5 zeolite and self-assembly of the zeolite subunits in a Na2O·(3.3–3.4) SiO2 aqueous solution. Na2O·(3.3–3.4) SiO2 in the aqueous solution plays two roles in the synthesis, one is providing a moderate alkaline medium with a buffering effect for the desilication of ZSM-5 zeolite, and the other one is supplementing the silica source. The desilication of ZSM-5 zeolite was optimized by the adjustment of reaction temperature and time, and pH of the solution. TZM were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption/desorption (BET), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The characterization results show that the characteristics of ZSM-5 zeolite, such as double six-membered or five-membered ring subunits, were still preserved in TZM, and TZM possessed the well-ordered mesostructure of ZSM-5 zeolite crystals. Compared with the pure silica mesoporous molecular sieve (Si-MCM-41, 4 days), the hydrothermal stability of TZM (8 days) was increased by 100% in refluxed water. The significant improvement of TZM hydrothermal stability was due to an increase of the surface hydrophobicity and the ratio of 5-rings or 6-rings, and a remarkable decrease in the number of hydrophilic silanol groups. After hydrothermal treatment for 8 days, TZM also exhibited a more efficient catalytic activation than Si-MCM-41 treated for 4 days in the CO2 reforming of methane reaction at 1023 K (750 °C). The 5% Ni/TZM-8-Glu (5 wt% Ni, loading) catalyst prepared by a glucose modified impregnation method exhibited excellent catalytic activity, which provided 73% CH4 and 72.5% CO2 conversion at 1023 K (750 °C).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...