Phosphorescent cyclometalated iridium(iii) complexes: synthesis, photophysics, DNA interaction, cellular internalization, and cytotoxic activity†
Abstract
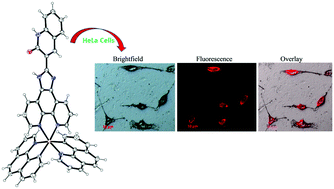
Iridium(III) complexes containing quinoline-appended polypyridyl ligands [Ir(ppy)2(qip)]+ (1) and [Ir(bhq)2(qip)]+ (2) {ppy = 2-phenylpyridine, bhq = benzo[h]quinoline, Qip = 2(1H)-quinolinone-3(1H)-imidazo[4,5f][1,10]phenanthrolin-2-yl} have been synthesized and characterized. The structure of complex 2 has been determined by single crystal X-ray crystallography. The experimental photophysical properties of the complexes have been compared with the theoretically obtained results by density functional theory (DFT) and time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) studies. The HOMO of the complexes is mainly localized on the iridium atom while the LUMO is mainly localized on the proximal position of the N–N donor polypyridyl ligand and the LUMO+1 is localized on the distal portion of the N–N donor polypyridyl ligand. The binding of complexes to double-stranded calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) has been investigated by absorption and emission spectroscopic techniques. The electrophoretic mobility shift assay of plasmid DNA in the presence of complexes shows DNA aggregation at micro-molar concentration. These complexes have low toxicity and their strong intracellular luminescence highlights their potential as theragnostic agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...