A nanosensor made of sulfur–nitrogen co-doped carbon dots for “off–on” sensing of hypochlorous acid and Zn(ii) and its bioimaging properties†
Abstract
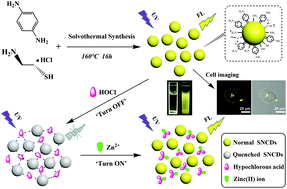
In this study, we present a facile one-step solvothermal strategy for the fabrication of sulfur–nitrogen co-doped carbon dots (SNCDs) using p-phenylenediamine and cysteamine hydrochloride as the precursors. The as-prepared SNCDs possess well monodispersed and nearly spherical morphology, and present favorable optical performances encompassing strong yellow-green fluorescence and excitation wavelength-independent fluorescence behavior with the maximum excitation/emission wavelength at 420/550 nm. More strikingly, the emission of SNCDs is effectively quenched by hypochlorous acid (HOCl/ClO−), whereas the SNCDs–HOCl aggregate can be released by zinc(II) ions (Zn2+) causing a fluorescence enhancement/recovery process. As such, we designed a SNCD-based fluorescence “off–on” nanosensor for HOCl and Zn2+ detection. The “turn off” mode enables the quantitative analysis of HOCl with a linear range of 0.18–4.22 μM and a detection limit of 0.021 μM. And the quantitative range for Zn2+ detection based on the “turn on” process is from 8.41 to 84.12 μM with a detection limit of 0.30 μM. Moreover, the fluorescent nanoprobe was applied for the assay of HOCl/ClO− and Zn2+ in water samples with satisfactory recovery values and in MCF-7 cell imaging with negligible autofluorescence, indicating its promising application potential in chemical, environmental and biological systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...