A hierarchical functionalized biodegradable PLA electrospun nanofibrous membrane with superhydrophobicity and antibacterial properties for oil/water separation†
Abstract
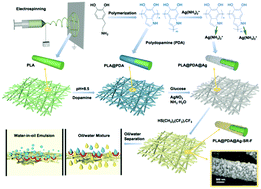
In recent years, the application of superwettability materials in oil/water separation has been developed rapidly. In this work, a hierarchical surface-modified biodegradable electrospun nanofibrous poly(lactic acid) (PLA) membrane was fabricated with the bioinspired coating of polydopamine (PDA), the immobilization of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and the subsequent superhydrophobization of the fluorinated thiol as a medium for high-efficient oil/water separation. Due to the synergistic effect of the hierarchical rough structure and the low surface energy chemicals, the as-prepared membrane exhibited superhydrophobicity (water contact angle = 158.6° ± 1.2°, sliding angle = 2.5° ± 0.2°) and superoleophilicity (oil contact angle = 0°). A high permeation flux (2664.3 ± 48.2 L m−2 h−1) and desirable separation efficiency (98.4 ± 1.0%) were achieved during the gravity-driven oil/water separation. Moreover, the membrane could separate the water-in-oil emulsion effectively. Furthermore, the stable hydrophobicity and roughness were maintained after 20 cycles of repeated separation, indicating the favorable recyclability. Besides, the membrane showed extremely low water-adhesion performance, desirable antifouling properties and superior antibacterial properties (antibacterial activity reached 99.0 ± 0.4%), which would make it a promising biodegradable candidate for oily wastewater treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...