Protecting electrochemical degradation of pure iron using zinc phosphate coating for biodegradable implant applications†
Abstract
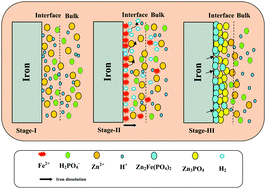
The surface of pure iron was modified with the formation of a zinc phosphate coating via a chemical conversion method for biomedical applications. The zinc phosphate coating is likely to decrease the rate of corrosion of pure iron during the initial periods of implantation, eliminate the risks associated with the excessive leaching of ferrous ions beyond a threshold level, and avoid the formation of excessive amounts of degradation products that could be harmful to wound healing, particularly during the early stages post-operation. A mild acidic solution containing zinc and phosphate ions was used as the electrolyte for the deposition of zinc phosphate coatings. The coatings were deposited by a chemical conversion method at 70 °C for 60 min. They were characterized for their morphological and structural characteristics by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction measurements. The functional groups present in the coatings were ascertained by Fourier-transform infrared and Raman spectroscopy. The corrosion behavior of uncoated pure iron and zinc phosphate-coated pure iron in the Hanks’ balanced salt solution (HBSS) was evaluated by potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, while their long-term stability was determined by immersion in HBSS at 37 ± 1 °C for 168 h. The bioactivity of zinc phosphate-coated pure iron was analyzed by immersion in simulated body fluid at 37 ± 1 °C for 240 h. The findings of the study reveal that surface modification of pure iron with a zinc phosphate coating is a useful approach toward the development of iron-based degradable implants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...