A bimetallic nanoparticle/graphene oxide/thionine composite-modified glassy carbon electrode used as a facile ratiometric electrochemical sensor for sensitive uric acid determination
Abstract
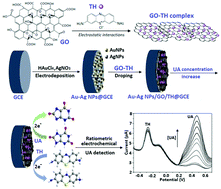
A novel and facile ratiometric electrochemical sensor was developed for the sensitive determination of uric acid (UA). Using one-step co-reduction of HAuCl4 and AgNO3 (as precursors) under cyclic voltammetry scanning, gold–silver bimetallic nanoparticles (Au–Ag NPs) were electrodeposited on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Through electrostatic interactions, self-assembly of graphene oxide (GO) and thionine (TH) occurred to form a GO–TH complex. The complex was drop-coated on Au–Ag NPs to prepare the Au–Ag NPs/GO/TH@GCE sensing platform through interactions among different components. The electrochemical signal responses of the sensing platform were recorded by square wave voltammetry measurements. With the increase of UA concentration [UA], the redox current peak intensity of UA (IUA at 0.46 V) increased regularly and that of TH (ITH at −0.28 V) was almost unchanged. The relationship between IUA/ITH and [UA] (1–100 μM) was linearly plotted (R2 = 0.9929), with a low detection limit of 0.3 μM. A facile sensor was fabricated based on the sensing platform and enabled sensitive ratiometric electrochemical sensing of UA in real human serum and urine fluids, over potential interferents. The experimental results confirmed high detection stability and recoveries of this sensor, indicating its high feasibility for UA detection in biological fluids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...