Green synthesis of Pt–Pd bimetallic nanoparticle decorated reduced graphene oxide and its robust catalytic activity for efficient ethylene glycol electrooxidation†
Abstract
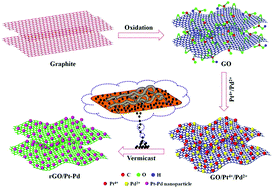
A simple one-pot green synthesis method is developed to prepare a platinum–palladium (Pt–Pd) bimetallic nanoparticle decorated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposite using vermicast extract as a reducing and stabilization agent. Morphological analysis confirms the homogenous decoration of Pt–Pd nanoparticles over the rGO sheets. Structural studies verify that the fatty acids and amide groups of the vermicast extract play a foremost role in the reduction of graphene oxide (GO) and the metallic ions. Benefiting from bimetallic features and a precise carbon support, the dehydrogenation of ethylene glycol (EG) and CO tolerance toward EG oxidation is significantly enhanced for rGO/Pt–Pd. The enhanced electrocatalytic activity of rGO/Pt–Pd toward EG oxidation is quantified via its mass activity of 803.4 mA mg−1, which is higher than the prepared nanocatalysts and commercial Pt/C. Furthermore, rGO/Pt–Pd retains a high current density (85%) over 500 cycles from its initial value, revealing its robust tolerance against CO poisoning. Thus the adopted green approach affords a cost-efficient and biocompatible carbonaceous metal nanocomposite with desirable electrocatalytic activity and stability for EG electrooxidation, demonstrating its wide applicability in high performance energy conversion devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...