Mixed polymeric micelles as a multifunctional visual thermosensor for the rapid analysis of mixed metal ions with Al3+ and Fe3+†
Abstract
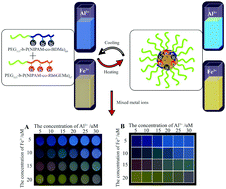
A novel type of responsive mixed double hydrophilic block copolymer (DHBC)-based multifunctional visual thermosensor (with mixed copolymers of poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-2,4-methacryloyl benzaldehyde oxime), (PEG-b-P(NIPAM-co-BDMa)) and poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-rhodamine 6G methyl acrylic acid) (PEG-b-P(NIPAM-co-Rh6GEMa))), for the detection of Al3+ and Fe3+ was designed and synthesized based on reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. Studies on the sensing processes showed that the multifunctional visual thermosensor has excellent selectivity for Al3+ and Fe3+ ions over many environmentally relevant ions, and high sensitivity with a detection limit on the nanomolar scale. Moreover, the multifunctional visual thermosensor can form micelles with (P(NIPAM-co-BDMa)/P(NIPAM-co-Rh6GEMa)) blocks as the cores and well-solvated PEG blocks as the coronas upon an increase in the temperature, which can enhance the detection sensitivity of Al3+ and Fe3+ ions. The detection limits using 0.05 g L−1 mixed micelles for the analysis of Al3+ and Fe3+ ions decreased from ∼5.95 to ∼4.02 nM, and ∼30.30 nM to ∼23.84 nM, respectively, upon changing the temperature from 25 °C to 40 °C. Furthermore, the mixed micelles in combination with Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and linear regression analysis to establish prediction models were used to achieve the successful quantitative detection of the mixed ions with Al3+ and Fe3+.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...