Boronic acid-functionalized iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles via distillation–precipitation polymerization and thiol–yne click chemistry for the enrichment of glycoproteins
Abstract
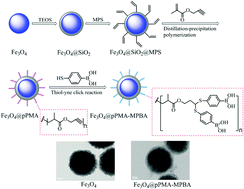
In this work, a novel strategy is developed for the fabrication of phenylboronic acid functionalized iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) via distillation–precipitation polymerization and thiol–yne click chemistry. Firstly, silica was coated on the Fe3O4 MNPs using a sol–gel method to obtain Fe3O4@SiO2. Subsequently, the vinyl groups were grated onto the silica-modified Fe3O4 surface using 3-methacryloyloxypropyltrimethoxysilane. Next, alkynyl groups as the clickable sites were modified on the MNPs to obtain the product Fe3O4@pPMA via distillation–precipitation polymerization of the vinyl end groups with propargyl methacrylate, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate. Finally, phenylboronic acid was grafted on the surface of Fe3O4@pPMA via thiol–yne click chemistry. The morphology, structure, and composition of all the synthesized phenylboronic acid functionalized Fe3O4 MNPs (Fe3O4@pPMA-MPBA) were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Three glycoproteins ovalbumin, transferrin, and horseradish peroxidase and two non-glycoproteins lysozyme and horse heart cytochrome are the chosen target proteins and their adsorption performance on Fe3O4@pPMA-MPBA is investigated. The Fe3O4@pPMA-MPBA MNPs exhibited outstanding advantages towards glycoproteins including high adsorption capacity, excellent specificity, repeatability and good enrichment recovery. Furthermore, the Fe3O4@pPMA-MPBA MNPs could efficiently enrich glycoproteins from real egg white samples. This study provides a feasible strategy for the surface functionalization of boronate affinity nanomaterials for the selective isolation and enrichment of glycoproteins.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...