ZnO nanoparticle-embedded silk fibroin–polyvinyl alcohol composite film: a potential dressing material for infected wounds
Abstract
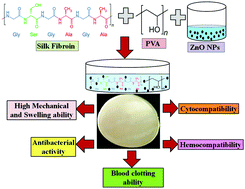
Wound dressing materials designed from biocompatible and biodegradable polymers are widely used in wound healing. The present investigation deals with the preparation of a unique blend of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) embedded in a silk fibroin–polyvinyl alcohol (SF–PVA/ZnO) composite film. Physical and chemical characterizations of the synthesized ZnO NPs and the prepared composite films (SF–PVA and SF–PVA/ZnO) were studied. Field emission scanning electron microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry confirmed that ZnO NPs were embedded in the SF–PVA composite film. The SF–PVA/ZnO composite film showed enhanced mechanical properties due to ZnO NPs. The study of antibacterial activity of the prepared composite films revealed that the embedded ZnO NPs showed excellent antibacterial activity against microorganisms that cause wound infections. The SF–PVA/ZnO composite film showed enhanced swelling behavior and faster blood clotting ability compared to the control SF–PVA composite film. The in vitro cytocompatibility study exhibited the nontoxic nature of the synthesized SF–PVA/ZnO composite film. These studies confirmed that the designed composite film holds huge potential to be used as a dressing material for infected wounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...